disk3D
Creates a new disk in ℝ³.
Syntax
-
disk3D([a[, f[, d[, α]]]])-
ais a three-dimensional real vector -
fis a three-dimensional real vector -
dis a three-dimensional real vector -
αis a real number
-
Description
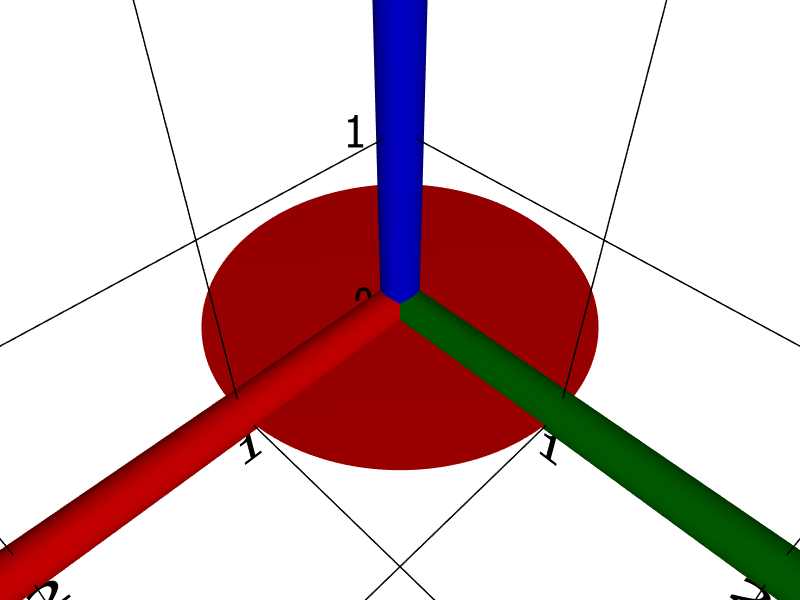
disk3D() creates a circular disk of radius 1 centred at the origin with normal direction ❨0, 0, 1❩.
disk3D(a, f, d, α) translates the disk by a, scales it by diag(f), aligns its normal with d, and rotates it an amount α about its (normal) axis.
Since a disk is flat, the third component of f should be unity. Unless the two first components of f coincide, the resulting object will be a non-circular elliptic disk.
Hence,
-
aspecifies the position of the disk’s centre. -
f = (s, t, 1)specifies the half-axis lengthssandtof the (elliptic) disk. -
dspecifies the normal direction of the disk. -
αspecifies the rotation of the disk about its (normal) axis.
If omitted, a defaults to ❨0, 0, 0❩, f to ❨1, 1, 1❩, d to ❨0, 0, 1❩, and α to 0.
The object is shown in the current scene and a reference to the object is returned.
The AdjustVisual function can be used to adjust the appearance of the disk. See Visual settings for a list of applicable settings.
Examples
disk3D()