cone
Creates a new cone.
Syntax
-
cone([a[, f[, d[, α]]]])-
ais a three-dimensional real vector -
fis a three-dimensional real vector -
dis a three-dimensional real vector -
αis a real number
-
Description
cone() creates a circular cone (quadratic surface) with radius 1 and height 1 parallel to the z axis, extending from z = 0 (apex) to z = 1.
cone(a, f, d, α) translates the cone by a, scales it by diag(f), aligns it with d, and rotates it an amount α about its axis.
Hence,
-
aspecifies the position of the cone’s apex. -
f = (s, t, h)specifies the half-axis lengthssandtand heighthof the cone. -
dspecifies the axis of the cone (considered as an arrowhead, the arrow will point in the−ddirection). -
αspecifies the rotation of the cone about its axis.
If omitted, a defaults to ❨0, 0, 0❩, f to ❨1, 1, 1❩, d to ❨0, 0, 1❩, and α to 0.
The object is shown in the current scene and a reference to the object is returned.
The AdjustVisual function can be used to adjust the appearance of the cone. See Visual settings for a list of applicable settings.
Examples
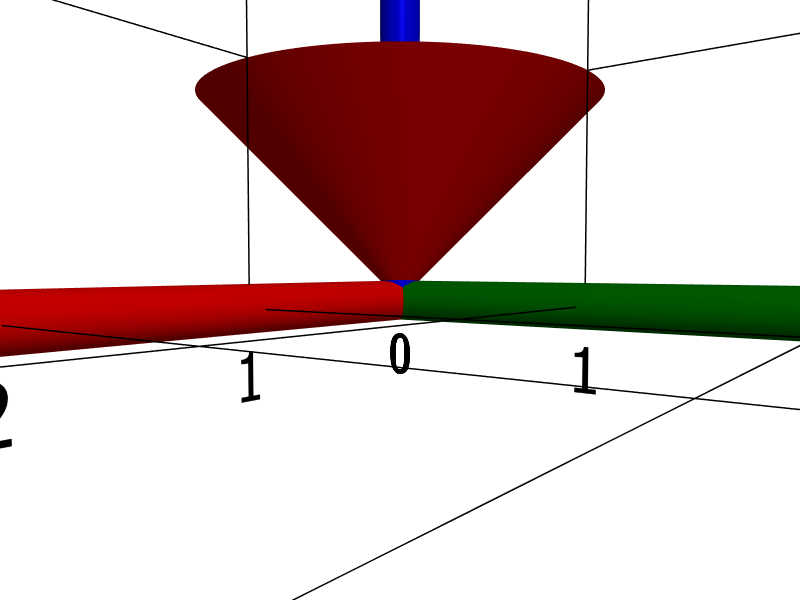
cone()
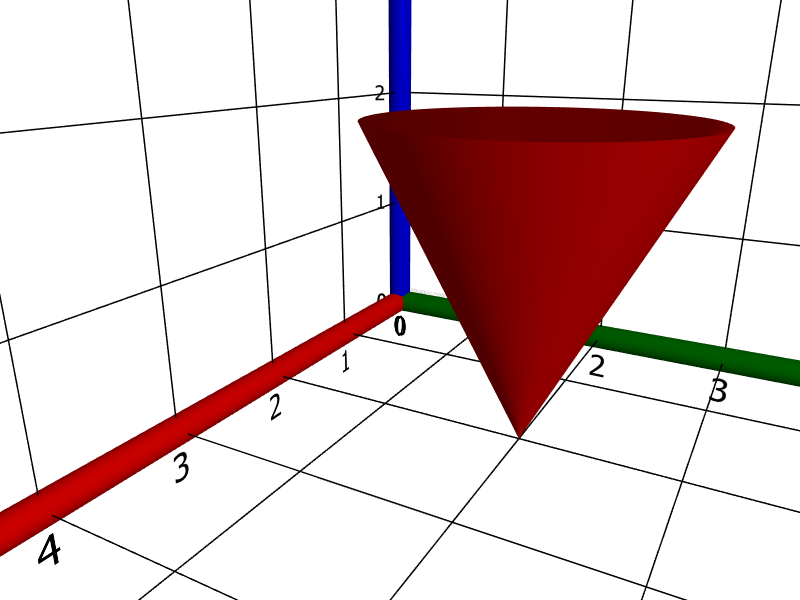
cone(❨2, 2, 0❩, ❨1, 1, 2❩)
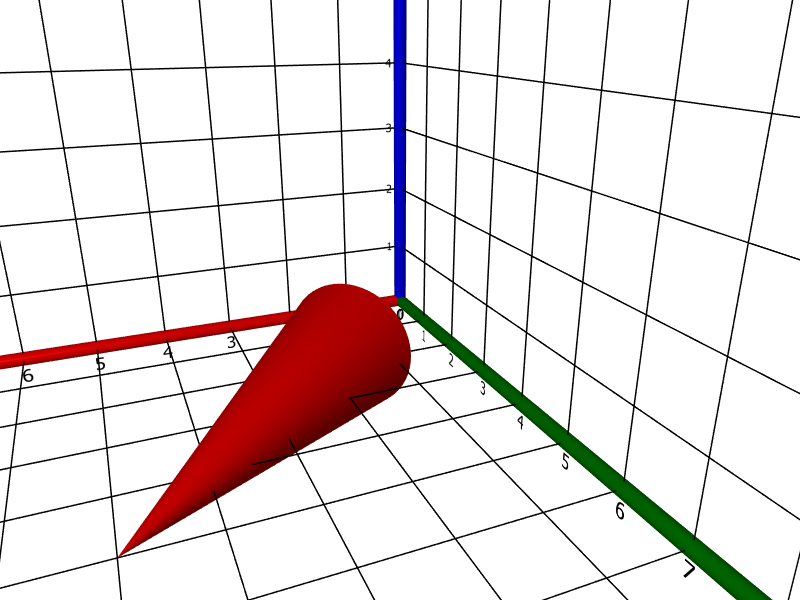
cone(❨5, 5, 0❩, ❨1, 1, 5❩, ❨−1, −1, 0❩)
Notes
To create a solid cone, use solid("cone") instead.