arrow
Creates an arrow (vector) in a diagram or scene.
Syntax
-
arrow(v)-
vis a vector
-
-
arrow(a, v)-
ais a vector -
vis a vector
-
-
arrow(a, "to", b)-
aandbare vectors
-
Description
If v is a two- or three-dimensional real vector, then arrow(v) displays this vector in the current diagram or scene, based at the origin.
If a and v are two- or three-dimensional vectors (of the same dimension), then arrow(a, v) displays the vector v based at a in the current diagram or scene.
If a and b are two- or three-dimensional vectors (of the same dimension), then arrow(a, "to", b) displays the vector b − a based at a (thus pointing at b) in the current diagram or scene.
Examples
diagram("arrows");
[0, 15, 1] @ (n ↦ arrow(❨cos(2⋅π/16 ⋅ n), sin(2⋅π/16 ⋅ n)❩))
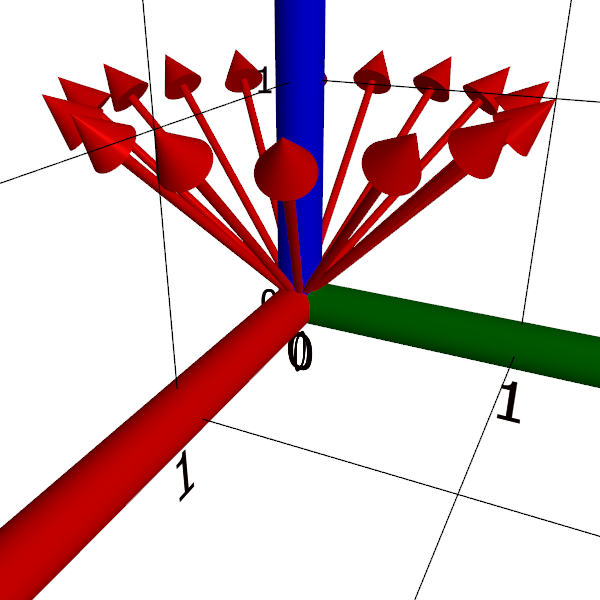
scene("arrows");
[0, 15, 1] @ (n ↦ arrow(❨cos(2⋅π/16 ⋅ n), sin(2⋅π/16 ⋅ n), 1❩))